Content Launcher Overview
Fire TV supports searching and launching content using a Fire TV remote, touch, or voice. The modality agnostic Content Launcher API supports searching, browsing, and playing content using different interfaces. All Content Launcher integrated apps should integrate the Account Login API to send your app's login status to the Fire TV. For API details, see Content Launcher API and Account Login API in the Vega API reference.
Content Launcher invokes the handleLaunchContent callback function through diverse modalities. Fire TV remote, voice commands, or future input methods like touch, stylus, or mouse triggers content searches, app launches, and deep linking (directly playing specific content). Your app remains compatible with both existing and upcoming input modalities, ideally without requiring recompilation. This forward-thinking approach provides longevity and flexibility in app design, accommodating technological advancements without necessitating significant code modifications.
Before you start
All catalog integrated apps must integrate the Content Launcher API. Catalog integration means describing your app's media using Amazon's Catalog Data Format (CDF), and then regularly uploading the catalog to Amazon's S3 bucket.
Fire TV uses the ingested content in multiple ways. For example, Fire TV's Universal Search and browse enables the discovery of movies and TV shows using the catalog-ingested content. Universal search and browse is not app specific, but rather "universal" across all apps that have ingested their catalogs into Amazon. Alexa uses ingested catalog content to search and play content over voice commands. When users say phrases like "Alexa, play Bosch from <app name>" or "Alexa, Search Bosch in <app name>", your app plays or searches for that media.
Universal Search and Browse on Fire TV
Universal Search and Browse enables users to discover your app's content on Fire TV, even if they don't have the app installed. Catalog file integrates your app's media's metadata into the Fire TV home screen and global search results. This catalog file enables your app's content to appear in users searches and in watch options on the content details pages.
Content discovery and Buy Box in Fire TV
Fire TV consolidates duplicate titles from different providers into a single entry through catalog integration. When a customer searches on Fire TV, your app's content appears in the results, even if the user hasn't downloaded your app. This feature is called Universal Search and Browse.
When a user selects a title from the search results, Fire TV displays the content details page. Customers can see different watch options to play the content, depending on their entitlement. Your app is promoted in watch options, even if a user doesn't have your app installed or has not subscribed to your service. This promoted option is the Buy Box. Fire TV automatically selects what it thinks is the best way for customers to view the content. Fire TV promotes titles in the Buy Box based on what apps a customer has installed and their entitlements. Entitled content always appears first in the Buy Box. After that, viewing options are prioritized by offer types, such as Free, Subscription, Rental, and Purchase.
User experience (UX) guidelines for Universal Search and Browse
Each time your app launches, publish the user's subscription status. The Account Login API publishes your app's login status. Depending on the login state, the Fire TV UI displays different view options. There are different subscription states possible, which include the following:
Unauthenticated State
In this scenario, the user has not signed in to the app. Fire TV displays a "Subscribe" option on the content detail page. When the user clicks it, the app launches, immediately directing the user to the sign-in or sign-up flow. After successful authentication, the selected content should begin playback. If the user hasn't installed the app, they are redirected to the app download page.
In the following example, the customer has no entitlement to watch the media titled Seabound in the app Streamz.
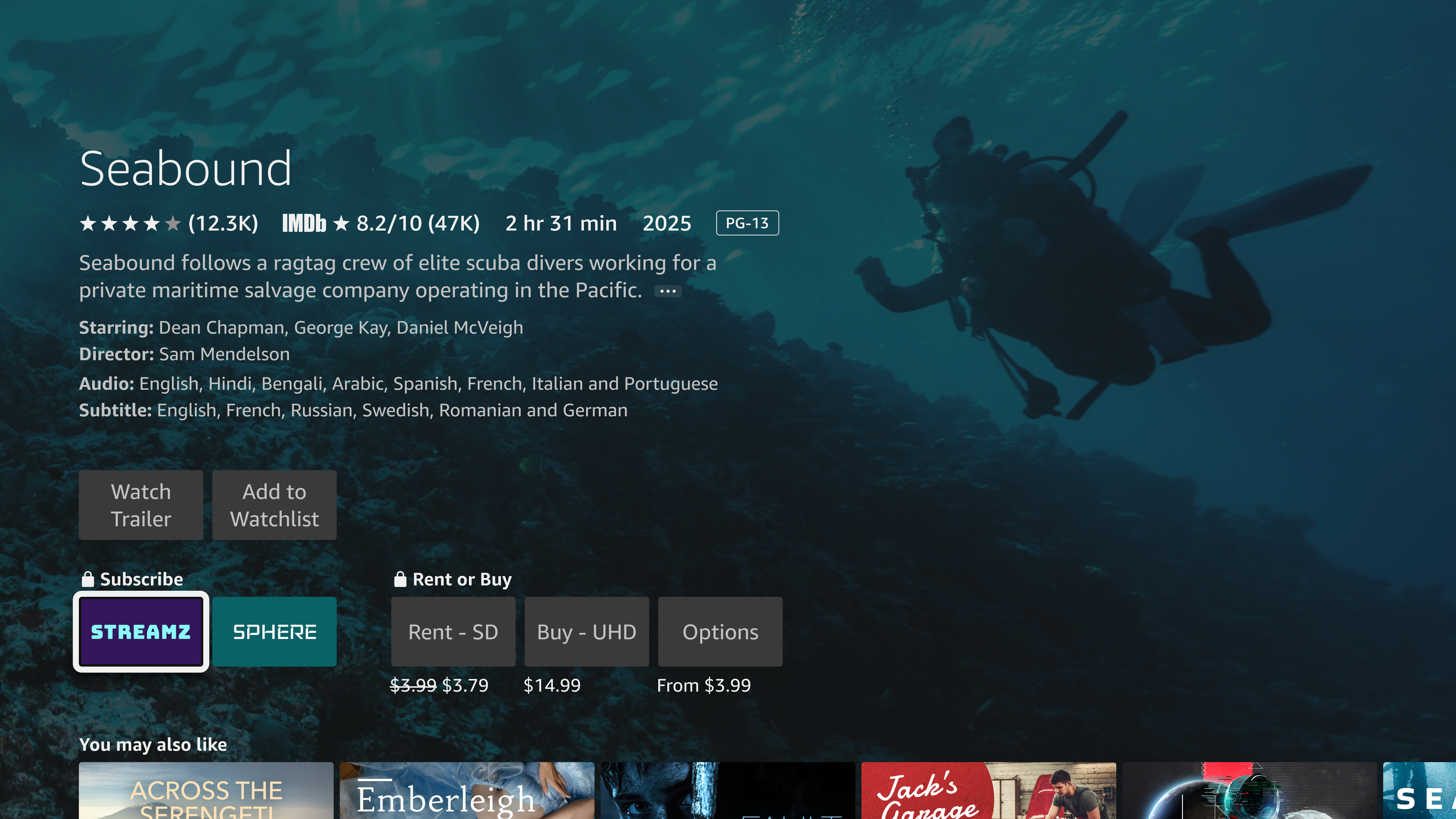
true. Not sending the status impacts the app's placement in the content details page.Authenticated state
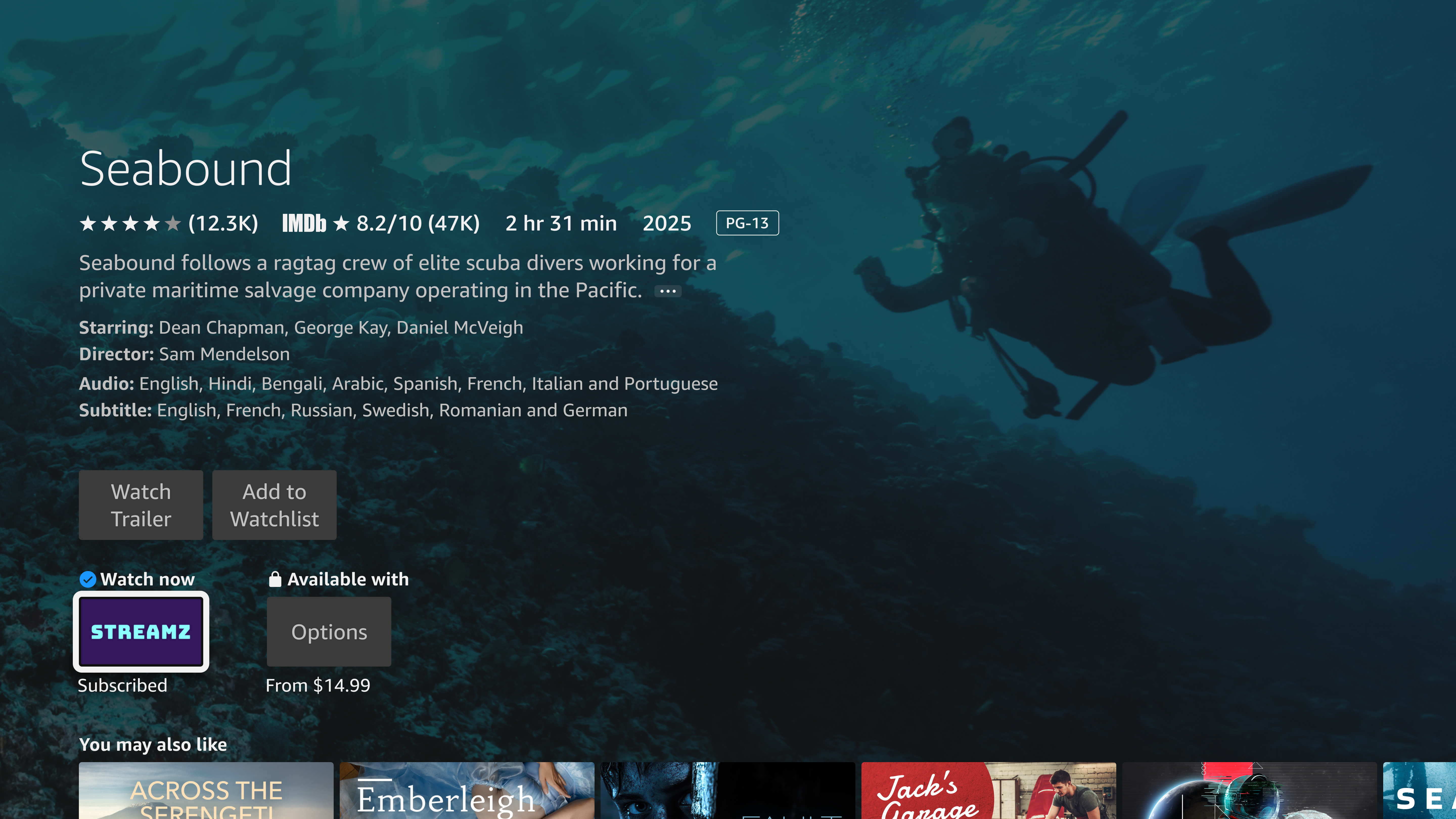
In this case, the user signed into the app already. The watch option appears as "Watch Now" in the content detail page. When the user selects the content, the app launches and begin playing the content.
In the following example, the customer is entitled to watch Seabound in the Streamz app.
Featured rows on the Fire TV home screen
Fire TV's home screen includes rows such as "Next up for you", "Recommended free movies and TV programs", "Latest movies", and more. Only Content Launcher integrated content is included in these featured rows. Content Launcher requires no additional integration to feature your content.
Voice capabilities in Fire TV apps
All the apps that have integrated their catalog should handle voice commands for search and play. Alexa enables Search and Play over voice on Fire TV. The user can use Alexa voice capabilities to easily discover and engage with content in your app without relying on a Fire TV remote. Alexa delivers voice requests directly to the app through the Content Launcher API.
Vega apps receive messages through the Content Launcher interface for play and search for the following:
-
Quick play. Users ask Alexa to play a video by saying, "Alexa, watch < title name >, " or "Alexa, watch < title name > on < app name >". Alexa launches the app and the app starts playing the requested title. Alexa uses your catalog to find the content requested by the user.
A user asks to play a specific episode in a show by saying, "Alexa, watch < Show Name >, Season < Number >, Episode < Number >." That specific episode plays directly instead of always playing episode one from season one.
-
In-app search. A user can perform a search in your app by saying, "Alexa, find < title name > on < app name >," or "Alexa, find < genre > on < app name >." Use your own logic to address the search requests within your app.
search and find utterances.-
Transport Control. Customers can control media playback through voice commands such as:
- "Alexa, play"
- "Alexa, pause"
- "Alexa, fast forward"
- "Alexa, fast forward 5 minutes"
- "Alexa, next"
- "Alexa, previous"
- "Alexa, rewind"
- "Alexa, resume"
- "Alexa, stop"
Vega Media Controls (KMC) enables seamless handling of Transport Control commands. Apps that use the W3C Media API for content playback benefit from built-in KMC integration. The W3C Media API automatically creates the KMC server, publishes server states, and handles voice Transport Control commands. These controls do not include the Next and Previous commands.
To enable Transport Control support through the W3C Media API, see W3C Media integration with Vega Media Controls.
For apps that do not use the W3C Media API, you can integrate Transport Controls using the Vega Media Controls API.
Last updated: Feb 17, 2026

