React Native for Vega App Architecture
This document outlines the React Native for Vega (RNV) architecture and serves as a reference for design choices and constraints, when building apps for Vega. See React Native Architecture documentation for more details about React Native framework.
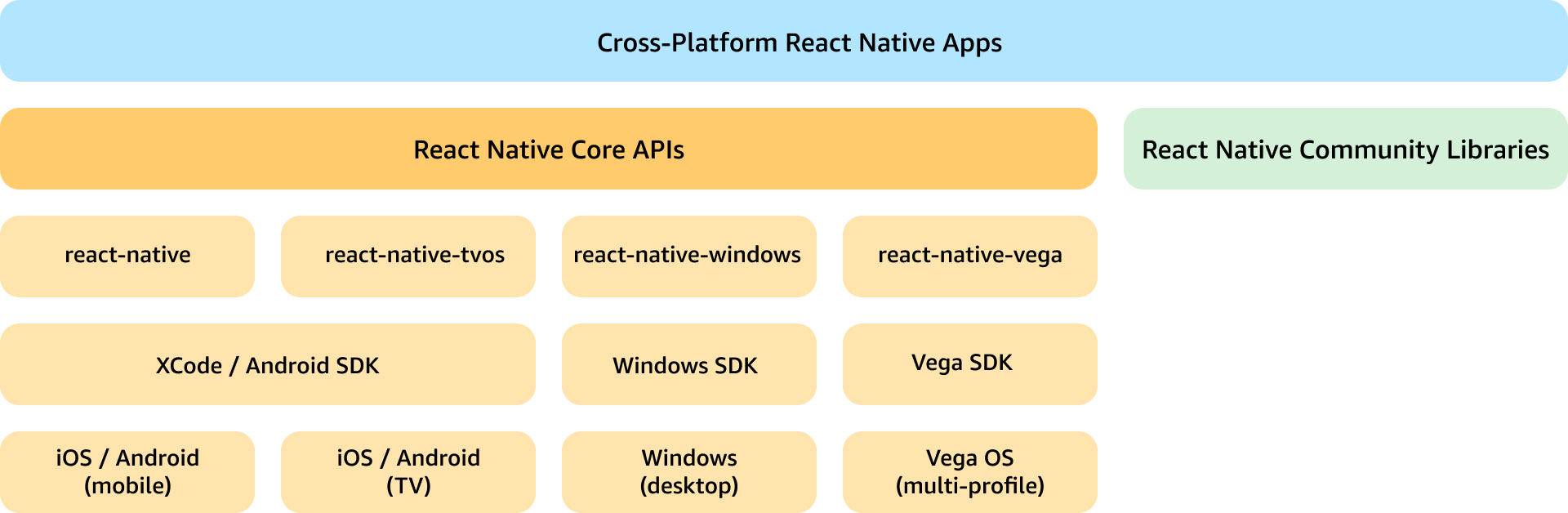
React Native (RN) for Vega is an out-of-tree fork of React Native framework for Vega devices, and provides familiar capabilities to develop React Native apps. React Native for Vega includes support for React Native core components and APIs, as well as a set of community supported libraries most commonly used by developers. Furthermore, for TV-specific functionalities, such as focus management, React Native for Vega incorporates most of the React Native tvOS capabilities.
Architectural tenets
Parity
React Native for Vega embraces the cross-platform principles of the React Native ecosystem, and aims to provide parity with RN APIs and popular libraries. RNV supports over 80% of RN core components and APIs. Additionally, RNV has ported over 40 RN libraries popular in the RN ecosystem. This support enables reuse of code across Vega OS and other OS platforms. RNV also includes APIs from RN tvOS to support focus management and event handling capabilities specific to TV devices. Additionally, where it makes sense, RNV includes specific APIs exclusive to a specific RN platform, such as BackHandler (Android), SafeAreaView (iOS).
The Vega SDK also includes support for common RN tooling and additional development and testing utilities to speed up app development while supporting a performant runtime. React Dev Tools, Chrome Dev Tool, Flashlight, and more are all available to use with RNV. You can leverage your existing workflows with these tools to work cross-platform.
Performance
Amazon designed React Native for Vega from the ground up to optimize for performance on Amazon devices. Your apps should meet Vega’s KPIs for performance.
Amazon built RNV with React Native's new architecture and benefits from all the improvements from RN core framework. The new architecture includes support for the following:
- Synchronous layouts and events
- Concurrent rendering
- Fast JavaScript and native interop over JSI, including support for Turbo Modules.
The Vega system image bundles the RN framework and runtime for RNV, instead of bundling it in the app packages. The Vega lifecycle manager leverages the system-bundled library to pre-warm processes assigned to apps for their cold start. This process improves the time-to-first-frame and the overall app load time. Additionally, Vega keeps the RN runtime in the shared memory space, which reduces the system memory footprint when you run multiple apps.
RNV also supports resource pressure events that applications can handle, to efficiently manage resource utilization in their applications. Developers can ensure their apps continue to run without affecting the system performance, as well as provide uninterrupted fluid experience to their users.
Vega's image system uses intelligent caching to improve performance. The image system tracks which UI components are visible and active, then optimizes memory usage both in RAM and on disk. This optimization helps images load and display quickly. The system also manages images directly in the graphics card's memory to reduce processing load. RNV apps automatically benefit from these performance features.
Multi-profile and multi-modal
React Native for Vega supports a diverse set of Amazon devices, including TVs and smart speakers. It uses flexible layouts to fit content on different screen sizes. The Platform API helps apps adjust to different device types at runtime. You can also customize features for specific devices during the app building process using Vega's build tools.
Your users can control Amazon devices in different ways: through voice, touch, or remote controls. React Native for Vega (RNV) supports all these control methods automatically. RNV components work with both touchscreens and remote control D-Pads. The framework also includes Alexa voice control, letting users navigate apps and control media with voice commands. For TV apps specifically, RNV provides special tools to handle remote control navigation and focus management.
Built on standards
RNV uses familiar web standards to build app features. While it aims to match React Native's usual APIs, it also incorporates W3C standards for core functions. For example, RNV uses W3C standards for media playback, making it easy to use many existing JavaScript media players. In upcoming releases, RNV adds support for WebCrypto and WebWorkers, also based on web standards. By using these widely-adopted standards, RNV makes it simple to use many JavaScript libraries originally created for web browsers in Vega apps.
Implementation
Amazon built React Native for Vega as an out-of-tree implementation of the React Native framework to support devices running Vega OS. RNV ported the React Native software stack including React Common, Yoga, and Hermes for Vega OS to run on top of Vega’s native UI framework. RNV uses React Native’s new architecture and only supports JSI for JavaScript to Native interfacing. RNV also supports the new Fabric renderer for synchronous layout and effect improvements and concurrent rendering. Additionally, RNV supports native integrations through Turbo Native modules and Fabric Native components for the Vega platform.
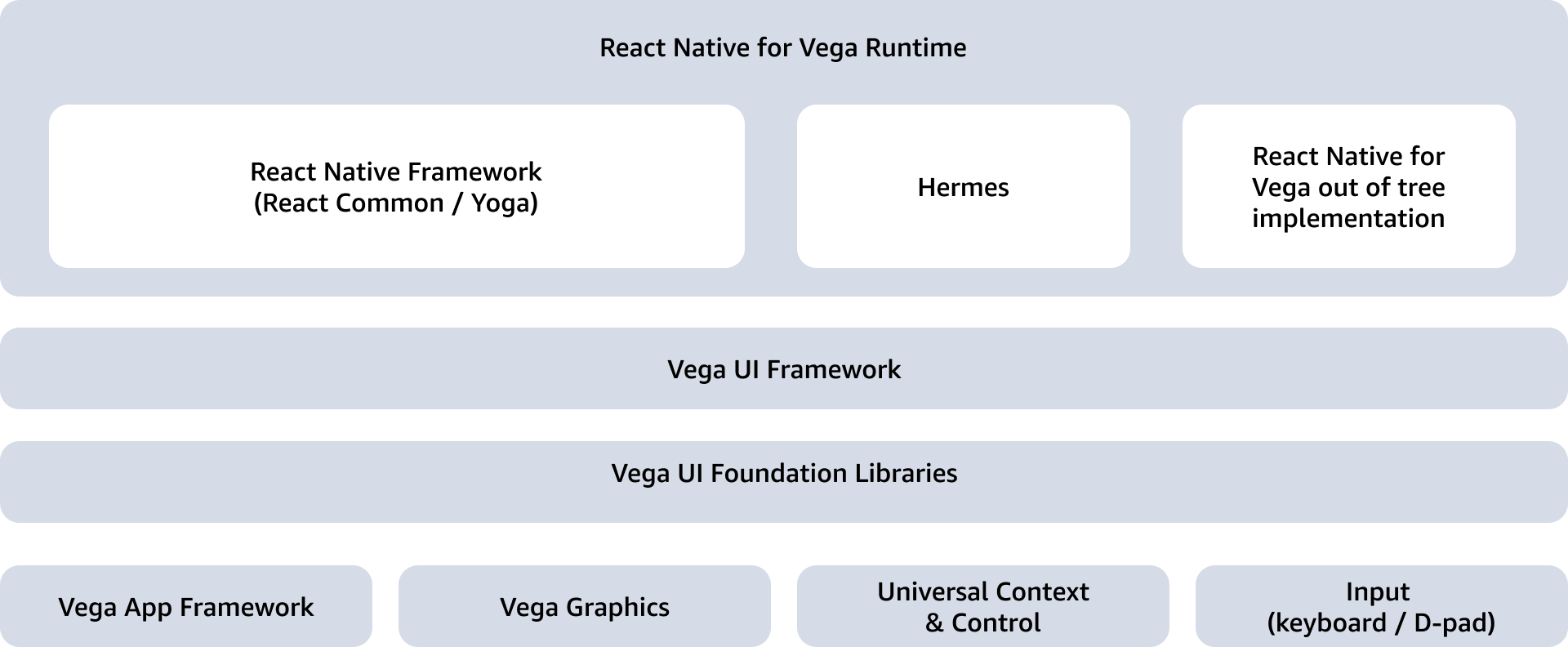
Built into the OS, dynamically linked
RNV makes a unique architectural choice by bundling the entire React Native runtime into the Vega OS, which dynamically links with the apps at runtime. Alternatively, the existing Vega platforms statically link the runtime with the app binary and bundle with the app code.
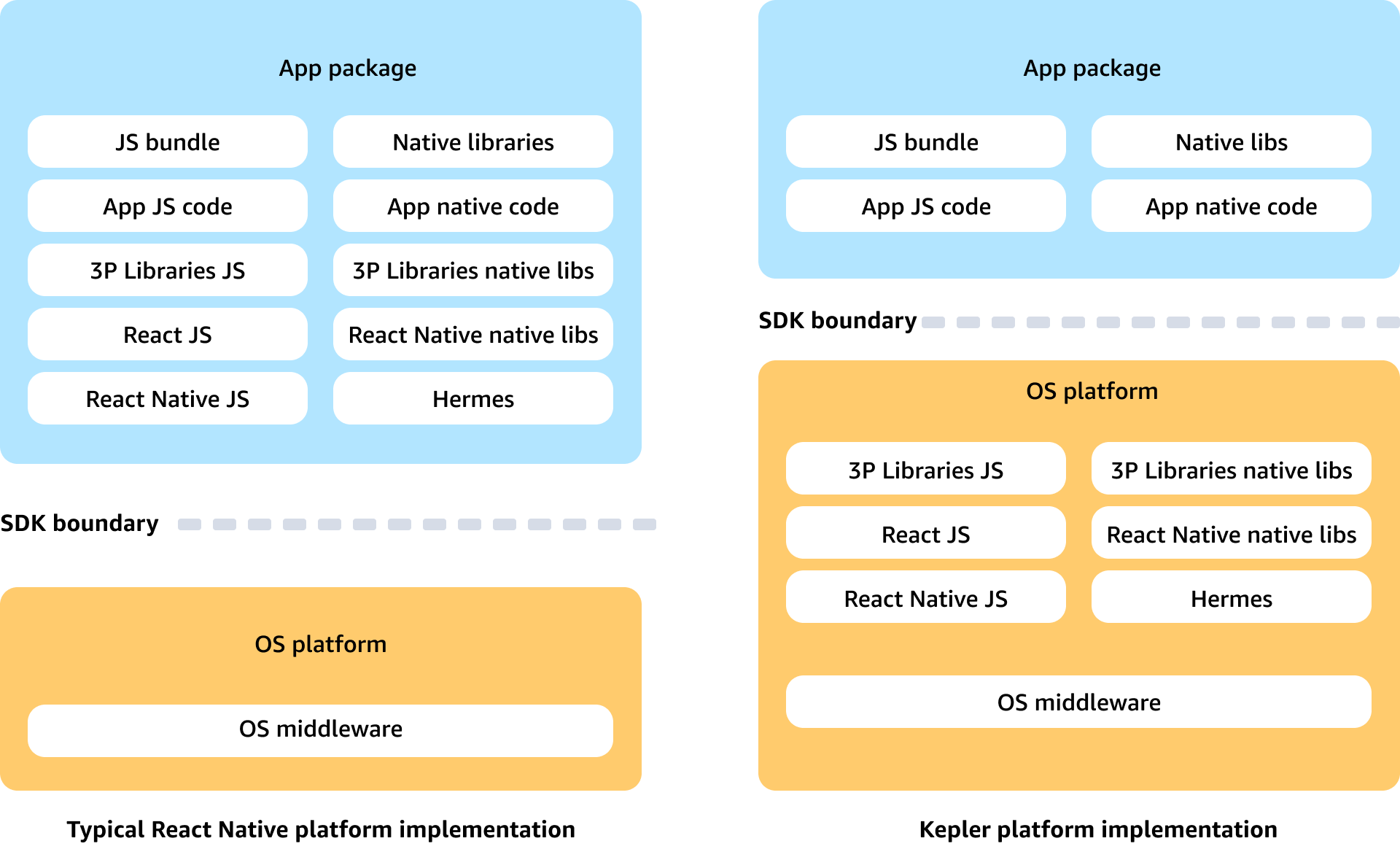
This opinionated choice of app architecture optimizes on-disk storage, startup and app switch times, and memory usage on devices running Vega OS. Removing the React Native runtime reduces the app bundle size by over 10MB. Loading the runtime from the OS also allows the Vega platform to pre-warm process pools with it, providing faster startup times for React Native apps.
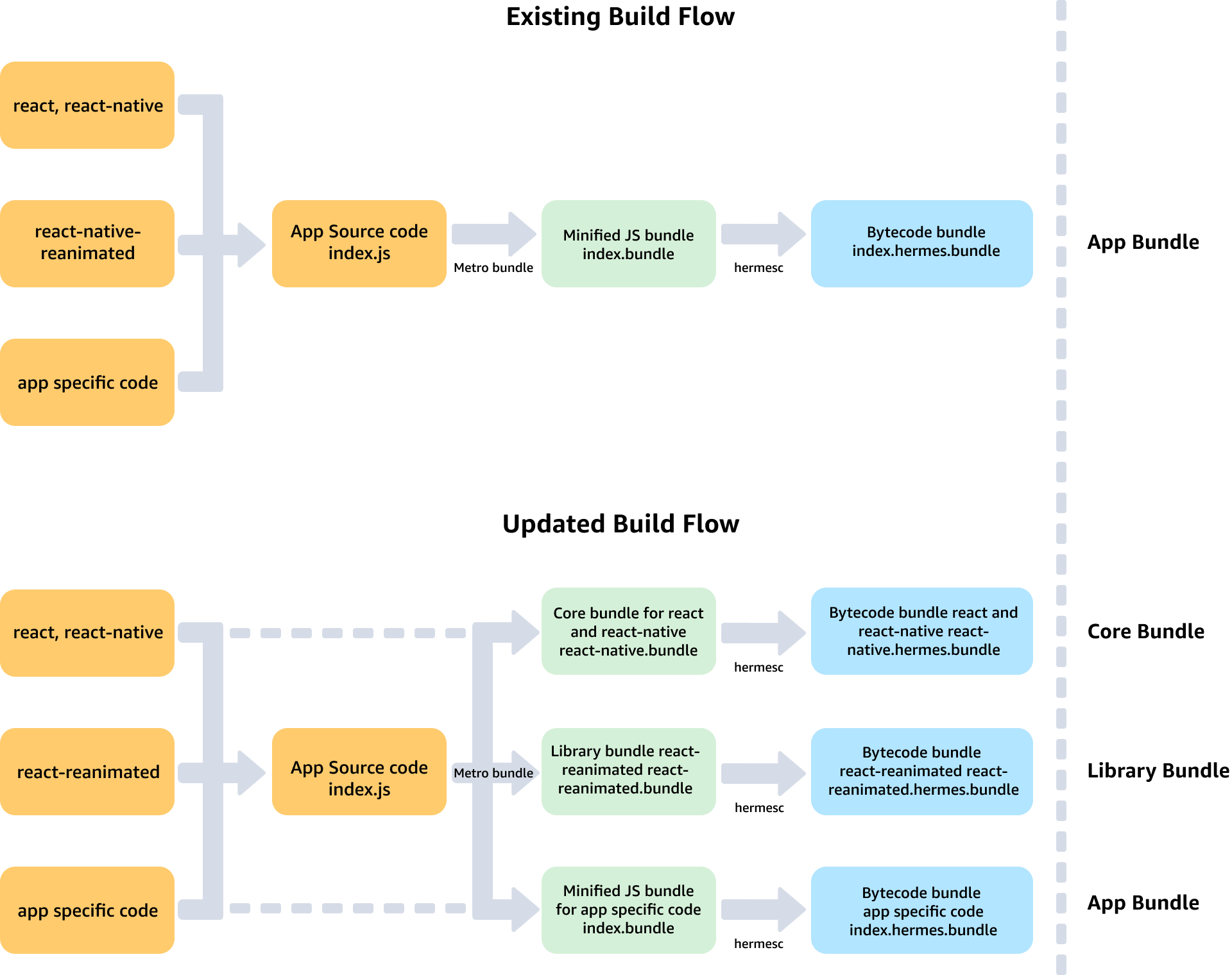
RNV also allows you to separate the main JavaScript code from the React and React Native libraries with split-bundling. Split-bundling reduces the app's size by 1-2 megabytes and ensures it works well with the device's operating system. When the app starts, it loads these separate React and React Native components along with the app's own code. This approach is similar to how the standard React Native runtime works.
API and ABI stability
Including React Native in the Vega operating system creates some challenges. When React Native releases new versions with breaking changes, apps might stop working correctly. Since Hermes (the JavaScript engine) changes how it handles code, JavaScript code must be recompiled for each new release. Other platforms that use React Native avoid these problems by packaging the React Native runtime with each app. This runtime ensures the app always uses its built-in version.
The current Vega operating system uses React Native version 0.72, with plans to update to a newer version soon. You need to check which React Native versions are available on Vega devices and set up your apps accordingly. Versioning helps ensure apps work properly on both current and future Vega devices and remain compatible with older versions.
RNV offers two main solutions to handle compatibility issues:
-
Dual Bundle Packaging: RNV includes both the compiled and raw JavaScript code in each app. Therefore, new version updates to a device with the JavaScript engine (Hermes), the Amazon Appstore automatically recompiles the app's code during installation.
-
Version Control System: You can specify both minimum required and preferred versions of app dependencies. This versioning helps the Appstore determine which devices can run the app. RNV also provides a tool called
isPresentOnOSto check if specific dependency versions are available on a device.
These features help apps continue working across different Vega device versions.
The RNV team is working with Meta (Facebook) to make React Native more stable. Meta recently released their first stable JavaScript API for React Native and plans to stabilize other features across all platforms. Soon, the Hermes JavaScript engine will be backward compatible. Once completed, RNV apps will work properly across all versions of Vega operating systems.
Headless JavaScript code
Vega supports running JavaScript code in the background through headless tasks and services. Headless tasks handle one-time operations that run independently, while headless services enable ongoing interaction between the UI and background processes. This architecture improves performance by moving resource-intensive operations like media playback and EPG data syncing off the main UI thread. Each headless component runs in its own JavaScript runtime instance powered by Hermes. The headless runtime is optimized with a minimal set of supported modules to maintain a small memory footprint. Apps can leverage this capability through APIs like the Headless JS Playback Service. This service has shown up to 30% improvement in time-to-first-video-frame by processing media separately from the UI.
Versioning and upgrades
Vega plans to release a new version of RNV once per year. The system supports three versions at a time, covering a three-year period. You can update your apps when you're ready, while keeping apps working across different device versions. You can specify which RNV version your app needs in your settings.
To save device storage and memory, only the two newest versions are preloaded. New tools are coming soon to help you upgrade your apps more easily between versions. New solutions are being sought to help developers who can't update their apps within the three-year window.
Last updated: Oct 30, 2025

